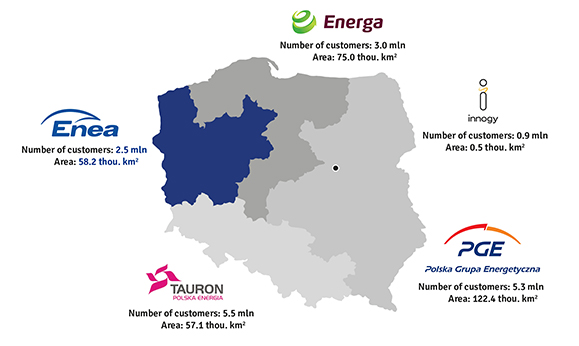
Areas of operation
In 1997, the process of the Polish electricity market demonopolisation started. The process led to the market division into the different areas: generation, transmission and distribution, and energy trading.
With time, in order to hedge the supply chain for the production area, the largest energy groups expanded their activity by the area of extraction.
Poland is the largest producer and selling market for bituminous coal among the European Union Member States. In the perspective of ten-odd forthcoming years, bituminous coal in Poland will be the primary raw material used for electric and heat energy production.
Bituminous coal for heating purposes in Poland jest extracted predominantly by the entities remaining under the control of the State Treasury. These include, without limitation, Jastrzębska Spółka Węglowa SA, Kompania Węglowa SA, Katowicki Holding Węglowy SA, Polska Grupa Górnicza sp. z o.o., and Tauron Wydobycie SA. In addition to the entities with the State Treasury shareholdings, the importance of private or privatised mines (e.g., LW Bogdanka) in the field of extraction has been rising in the recent years.
Most electricity on the Polish market is generated on the basis of conventional fuels, i.e., bituminous coal and lignite. However, in the recent years, Poland has seen a rising awareness of environmental damage caused by conventional energy, while its membership in the European Union provided an additional stimulus for restructuring the Polish power sector.
Renewable energy is received from natural recurring processes in the natural environment. Pursuant to the Power Law, renewable sources of energy are utilised in the process of transforming wind, solar, aerothermal, geothermal, hydrothermal, wave, sea current and tide, and river fall energy as well as energy from biomass, biogas from waste landfills, and biogas created in the processes of sewage discharge or treatment or the decaying of plant and animal residues stored.
The development of electricity generation from renewable sources results from the need to protect natural environment and reinforce power safety. The purpose of measures taken in this respect is to increase the volume of energy produced from renewable sources, support technological development and innovation, create the opportunities for regional development, and ensure higher degree of power supply safety, especially on a local scale.
As it follows from the obligations resulting, among others, from the 3 x 20 climate and energy package, Poland must achieve a 15% share of RES in energy consumption by 2020. Due to high investment costs, striving to increase the share of these energy sources in the overall national electricity production requires the employment of adequate support systems which warrant their systematic growth.
Electricity transmission means energy transport via transmission networks (to distribution networks or final recipients connected thereto). Electricity distribution means energy transport to final recipients with the use of distribution networks.
Pursuant to the Energy Law, carrying on the business activity in the field of electricity transmission or distribution requires a licence of the President of Energy Regulatory Office (ERO). The leading electricity distributors in Poland are: Enea Operator sp. z o.o., TAURON Dystrybucja SA, PGE Dystrybucja SA and Energa Operator SA.
Electricity trading is the business activity which requires obtaining a licence from the President of ERO and involves wholesale or retail energy trading. Electricity trading in Poland takes place in the following three main energy market segments: contract market, exchange market, and Balancing Market.
Electricity trading on the contract market takes place on the basis of bilateral contracts (agreements) signed between energy producers, companies trading in energy, and final Clients.
The exchange market includes trading at the Polish Power Exchange (PPE, Towarowa Giełda Energii SA). Power trading at PPE takes places mainly at the so-called Day-Ahead Market (DAM). DAM is run as at the day preceding the day during which the physical supply of electricity takes place.
The Balancing Market is a specific area of the power market where the differences between transactions concluded among individual market participants and the actual demand for electricity are balanced.